
Membership:
1. Director and Chief Physician Ayurmax Multispeciality Ayurveda Hospital and Panchkarmacentre.
2. Member, Bhartiya Chikitsa Parishad Uttarakhand.
3. Member National Integrated Medical Association, Dehradun.
4. Member Unesco Club, Dehradun.
5. Previously worked as Lecturer (Dept. of Shalya Tantra) and Hospital Incharge, Uttaranchal Ayurvedic College and Hospital, Rajpur, Dehradun.
6. Member, Dehradun Rashtriya Manav Adhikar foundation.
7. Member, National Sushruta Association.
8. Member, Society of wound management.
9. Member, UNESCO Doon valley central.
Education:
1. B.A.M.S. from S.D.M college of Ayurveda, Karnataka from RGUHS – 1996
2. M.S. from Ashwini Ayurveda College, Davangere – 2002
3. Fellowship in Anorectal diseases and Ksharsutra from Manipal University.
Career highlights:
1. Successfully submitted a thesis on ‘A Clinical Comprehensive Study on Chitraka and Apamaaga Kshara on internal hemorrhoids.
2. Received the Honour Of Active Member by Unesco Club, Dehradun.
3. Guest of honor, and Guest speaker in World Cancer day held in WIC Dehradun 4/2/2016.
4. Guest of honor in “Woundcon” International conference held in SDMCA, Hasson 2019
5. The International Association of Lion Club as Awarded the certificate of Appreciation on the Eve of National Doctore’s Day 1st July 2020 for his outstanding dedication and valuable contribution towards the nation.
Awards & Highlights:
1. Received “ASHVINI-2016 Award” by Sri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara college of Ayurveda & Hospital, Hassan.
2. Received “Aarogyam Excellence in Health Care Award- 2019” by the honorable Governor of Uttarakhand -Baby Rani Maurya.
3. Received TV 100 Healthcare Excellence Award for Best Ayurveda Physician.
4. Received I-next Uttarakhand excellence award 2023 by the honorable Ayush minister of Uttarakhand Mr. Dhan Singh Rawat
5. Received Page 3 Women’s Day Award 2019.
Dr. Rekha is the director of Ayurmax hospital and chief physician at panchakarma center. She is a skilled anorectal surgeon, Ksharsutra specialist and Gynaecologist.
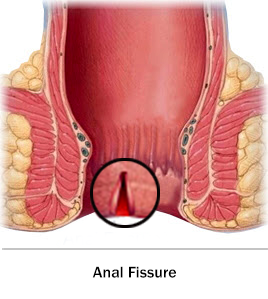
Fissure
An anal fissure is a common ano-rectal disorder that is characterized by a tear or crack in the skin lining the anus. Anal fissures can be caused by a variety of factors, including constipation, diarrhea, trauma, and childbirth. They can also occur as a result of certain medical conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease or sexually transmitted infections.
The symptoms of anal fissures can include pain, bleeding, and discomfort during bowel movements. The pain is often described as a sharp, burning sensation that can last for several hours after a bowel movement. Bleeding may occur when passing stools, and in severe cases, a small amount of blood may be present on the toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
Anal fissures can be diagnosed through a physical examination, including a visual inspection of the anus and a digital rectal exam. In some cases, additional tests, such as an anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
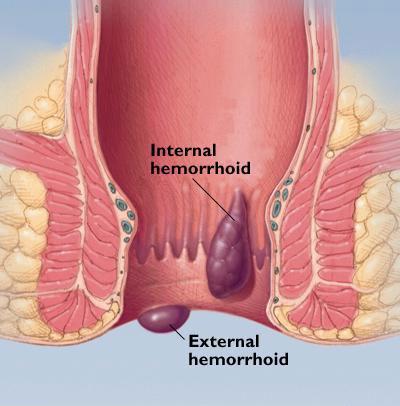
Hemorrhoids (piles)
Hemorrhoids, also known as
piles, are a common ano-rectal disorder that affects millions of people
worldwide. Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anus or rectum, which can cause
discomfort, pain, and bleeding.
There are two types of
hemorrhoids: internal and external. Internal hemorrhoids are located inside the
rectum and are not visible from the outside. External hemorrhoids are located
outside the anus and can be seen or felt as a lump or swelling.
The most common causes of
hemorrhoids are straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, and obesity. Other
factors that can increase the risk of hemorrhoids include a low-fiber diet,
constipation, diarrhea, and prolonged sitting or standing.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids can
include pain or discomfort in the anal area, itching or burning, swelling or a
lump around the anus, and bleeding during bowel movements. In some cases,
hemorrhoids may also cause a feeling of fullness or the urge to have a bowel
movement.
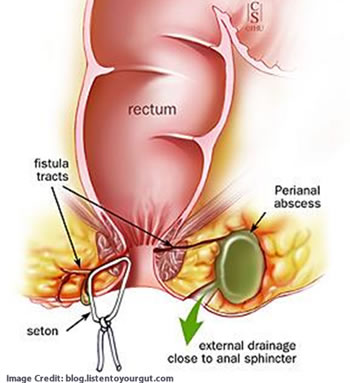
Fistula
An anal fistula is a type of ano-rectal disorder that occurs when a small tunnel forms between the anal canal and the skin surrounding the anus. Fistulas can develop as a result of an abscess, infection, or inflammation in the anal area. They can also occur as a complication of certain medical conditions, such as Crohn’s disease or tuberculosis.
The symptoms of anal fistulas can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and discharge from the anus. The discharge may be pus-like and have a foul odor. In some cases, a fever may also be present.
Diagnosis of anal fistulas involves a physical examination, including a visual inspection of the anus and a digital rectal exam. Additional tests, such as a fistulogram or an MRI, may also be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the location and severity of the fistula.
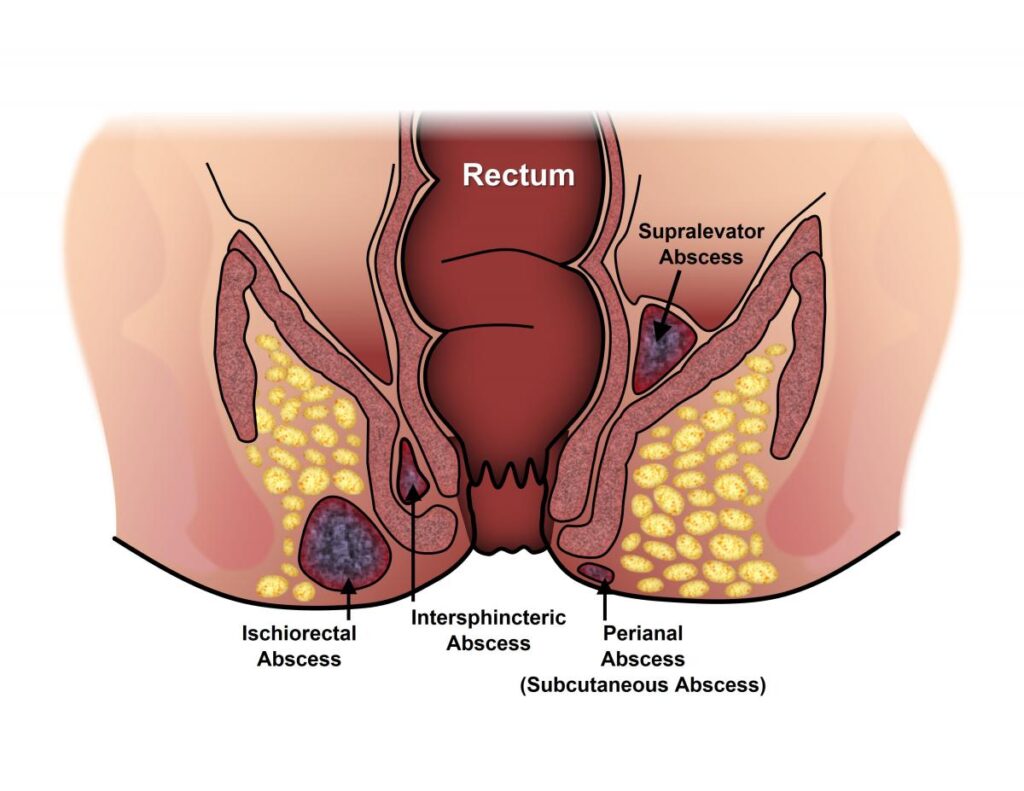
Peri-anal abscess
A peri-anal abscess is a type of ano-rectal disorder that occurs when an infection develops in the tissue around the anus. The infection can be caused by bacteria that are normally found in the colon, or it can be the result of an injury or other medical condition.
The symptoms of a peri-anal abscess can include pain, swelling, redness, and warmth around the anus. In some cases, a fever may also be present. The abscess may also drain pus, which can have a foul odor.
Diagnosis of a peri-anal abscess involves a physical examination, including a visual inspection of the anus and a digital rectal exam. Additional tests, such as an ultrasound or a CT scan, may also be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the location and severity of the abscess.
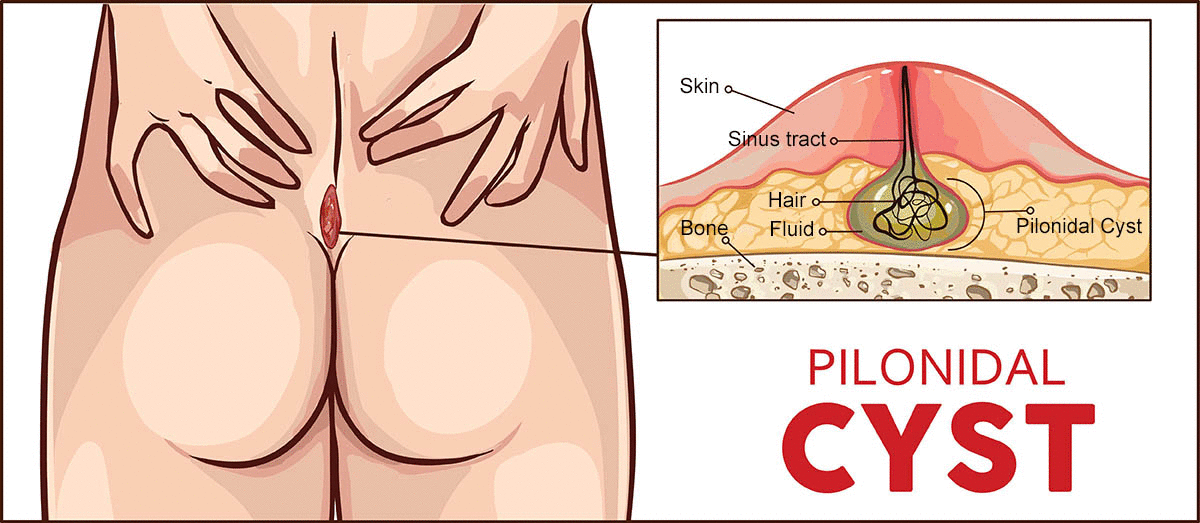
Pilonidal sinus
A pilonidal sinus is a type of ano-rectal disorder that occurs when a small tunnel or channel forms under the skin at the top of the buttocks, near the tailbone. The sinus is often filled with hair, skin debris, and other materials that can cause infection and inflammation.
The cause of pilonidal sinus is not completely understood, but it is thought to be related to the way that hair grows in the area. Pilonidal sinus can occur in people of all ages, but it is most common in young adults and men.
The symptoms of pilonidal sinus can include pain, swelling, redness, and discharge from the affected area. The discharge may be pus-like and have a foul odor. In some cases, a fever may also be present.
Diagnosis of pilonidal sinus involves a physical examination, including a visual inspection of the affected area. Additional tests, such as a CT scan or MRI, may also be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the location and severity of the sinus.
Qual polyps
A rectal polyp is a growth
that develops on the lining of the rectum or colon. Polyps can be either benign
(non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and they can vary in size and shape.
Qual polyps, also known as villous adenomas, are a type of rectal polyp that is
more likely to become cancerous than other types of polyps.
The cause of rectal polyps
is not completely understood, but they are thought to be related to a
combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors for developing
rectal polyps include a family history of polyps or colon cancer, inflammatory
bowel disease, and a diet high in fat and low in fiber.
The symptoms of rectal
polyps can vary depending on the size and location of the polyp. Small polyps
may not cause any symptoms, while larger polyps can cause bleeding from the
rectum, changes in bowel habits, and abdominal pain.
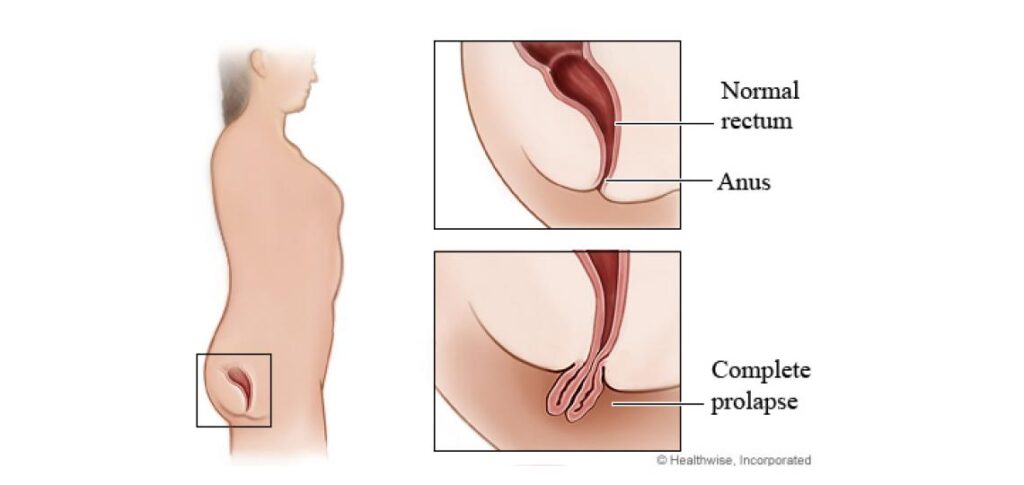
Rectal prolapse
Rectal prolapse is a medical condition that occurs when the rectum, which is the lower part of the large intestine, protrudes outside the anus. This can happen when the muscles and tissues that support the rectum become weakened or damaged, allowing the rectum to slip out of place.
The cause of rectal prolapse is not completely understood, but it is more common in women than in men and can be associated with conditions that cause chronic straining during bowel movements, such as constipation, chronic diarrhea, or long-term use of laxatives.
The symptoms of rectal prolapse can include a protrusion of the rectum outside the anus, pain, discomfort, bleeding, and difficulty with bowel movements. In some cases, there may also be fecal incontinence or leakage.
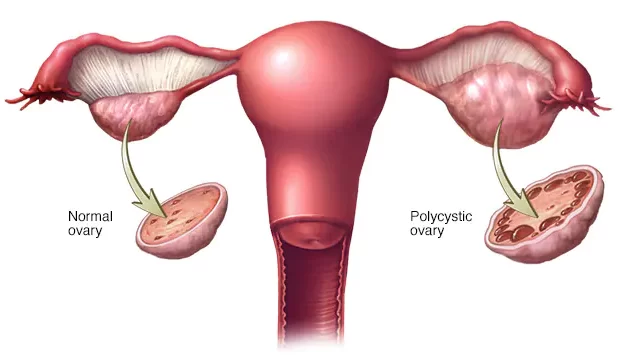
PCOS-PCOD
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
(PCOS), also known as Polycystic Ovary Disease (PCOD), is a hormonal disorder
that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by the growth of
multiple small cysts on the ovaries, which can cause irregular menstrual cycles
and fertility problems.
The exact cause of PCOS is
not known, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and
environmental factors. Insulin resistance, a condition in which the body does
not respond to insulin properly, is also thought to play a role in the
development of PCOS.
Symptoms of PCOS can vary,
but typically include irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth, acne,
weight gain, and difficulty getting pregnant. Women with PCOS may also have
high levels of androgens, male hormones that are normally present in small
amounts in women.
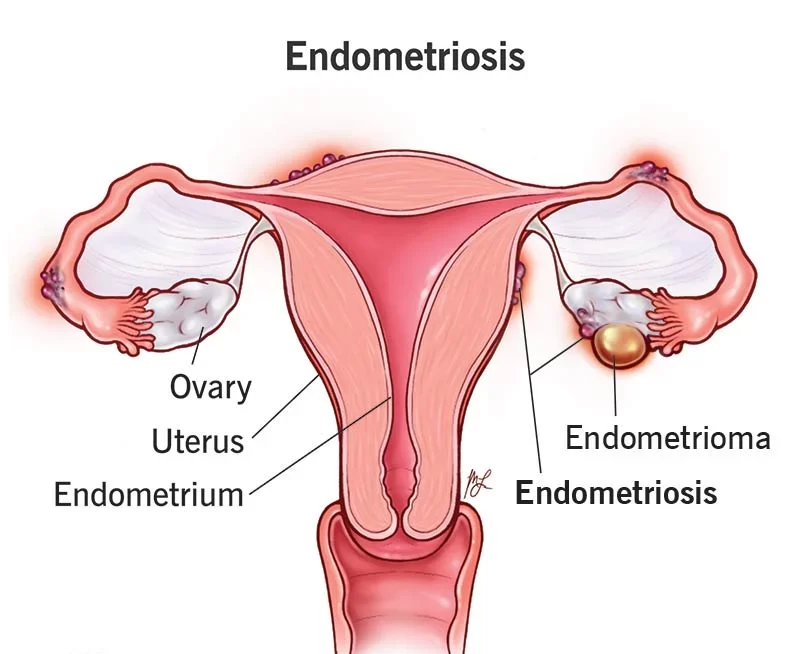
Endometrioma / Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus, known as the endometrium, grows outside of the uterus. This tissue can grow on other organs in the pelvic area, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and bladder, and can cause pain, inflammation, and scarring.
Endometrioma, also known as an ovarian endometrioma or chocolate cyst, is a specific type of endometriosis that occurs when endometrial tissue grows on the ovaries, forming a cyst filled with old blood. These cysts can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters and can cause pain, discomfort, and fertility problems.
The exact cause of endometriosis is not known, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Hormonal imbalances, particularly in estrogen, may also play a role in the development of endometriosis.
Symptoms of endometriosis can vary, but typically include pelvic pain, particularly during menstrual periods, pain during intercourse, and infertility. Women with endometrioma may also experience bloating, nausea, and fatigue.
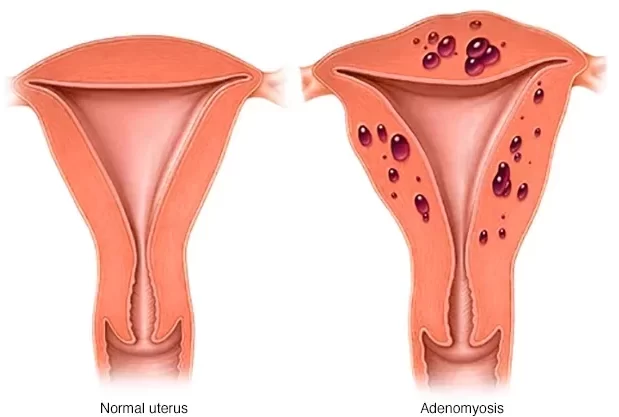
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a condition in which the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus, known as the endometrium, grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. This can cause the uterus to become enlarged and tender, and can lead to heavy, painful menstrual periods.
The exact cause of adenomyosis is not known, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Hormonal imbalances, particularly in estrogen, may also play a role in the development of adenomyosis.
Symptoms of adenomyosis can vary, but typically include heavy, prolonged menstrual periods, severe cramping and pain during periods, and pain during intercourse. Women with adenomyosis may also experience bloating, tender uterus, and fatigue.
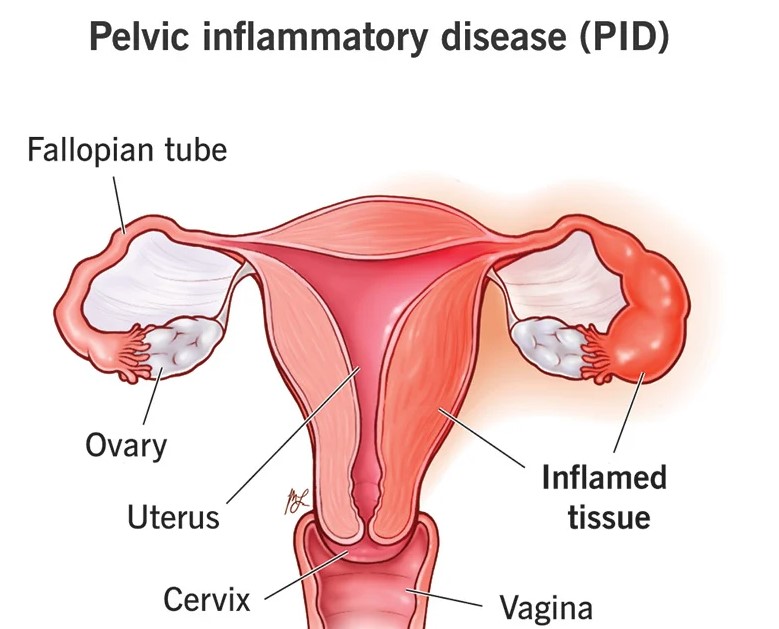
PID
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a condition in which the female reproductive organs become infected and inflamed, typically as a result of a sexually transmitted infection (STI) such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. The inflammation can cause scarring and damage to the fallopian tubes, leading to infertility or an ectopic pregnancy.
Symptoms of PID can vary, but typically include lower abdominal pain, pelvic pain, fever, unusual vaginal discharge, and pain during intercourse or urination. In some cases, there may be no symptoms at all.
Diagnosis of PID involves a physical examination, including a pelvic exam, and laboratory tests to identify the presence of bacteria or other pathogens. Imaging studies, such as an ultrasound, may also be used to evaluate the extent of the infection.
Infertility - Male / Female
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive a child after one year of unprotected intercourse. It affects both men and women, and can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic, hormonal, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Male infertility can be caused by a number of factors, including low sperm count or motility, abnormal sperm shape or function, and blockages or damage to the reproductive tract. Other factors, such as hormonal imbalances, genetic disorders, and certain medications or medical conditions, can also contribute to male infertility.
Female infertility can be caused by a number of factors, including hormonal imbalances, problems with ovulation or egg quality, damage to the reproductive tract, and age-related factors. Other factors, such as medical conditions, certain medications, and lifestyle factors, such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption, can also contribute to female infertility.

Tubal block – Uttarbasti
Tubal blockage is a condition in which the fallopian tubes, which connect the ovaries to the uterus, become blocked, preventing fertilization and pregnancy. Uttarbasti is an Ayurvedic therapy that is sometimes used to treat tubal blockage and improve fertility.
Uttarbasti involves the introduction of medicated oils or ghee into the uterus through the cervix. This is typically done using a special catheter or syringe, and the procedure may be repeated several times over the course of several weeks or months.
According to Ayurvedic theory, Uttarbasti can help to remove blockages in the fallopian tubes by promoting the flow of energy and fluids in the reproductive system. The medicated oils or ghee used in Uttarbasti are believed to have anti-inflammatory and nourishing properties that can help to improve the health and function of the reproductive organs.
While Uttarbasti may be effective for some women with tubal blockage, it is important to note that there is limited scientific evidence to support its use for this purpose. In some cases, tubal blockage may require surgical intervention, such as laparoscopic surgery or in vitro fertilization (IVF), to achieve pregnancy.
If you are experiencing fertility issues, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare provider who can help to diagnose the underlying cause and develop a personalized treatment plan. In some cases, a combination of traditional and alternative therapies may be recommended to help improve your chances of conception and pregnancy.
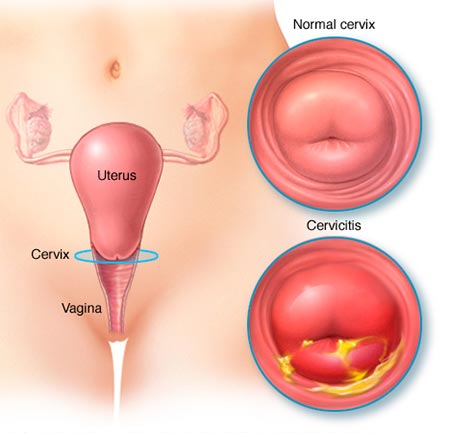
Ceavicitis / Cervical esosion
Cervicitis is a condition in which the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina, becomes inflamed. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, including vaginal discharge, pain during intercourse, and abnormal bleeding.
Cervical erosion, also known as cervical ectropion, is a condition in which the cells on the surface of the cervix are replaced by cells from the lining of the cervical canal. This can cause the cervix to become red and inflamed, and may lead to symptoms similar to those of cervicitis.
Both cervicitis and cervical erosion can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial or viral infections, such as chlamydia or herpes, hormonal imbalances, and certain medical procedures, such as cervical biopsies or IUD insertions.
Breast / Uterus (Malignancy)
Breast and uterine malignancies are two types of cancer that can affect women’s reproductive systems. Breast cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the breast tissue, while uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, develops in the lining of the uterus.
Breast cancer typically presents as a lump or thickening in the breast tissue, along with changes in the skin or nipple, such as dimpling or discharge. Uterine cancer may present as abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge, pelvic pain, or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
Risk factors for breast and uterine cancer include a family history of cancer, certain genetic mutations, obesity, and hormonal factors, such as early onset of menstruation or late onset of menopause.

Common gynecological disorders like Dysmenorrhoea, Menorrhagia, Metrorrhagia, Leukorrhea etc
Dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, metrorrhagia, and leukorrhea are common gynecological disorders that can affect women of all ages.
Dysmenorrhea refers to painful menstrual periods that can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, or pelvic inflammatory disease. Symptoms may include cramping, lower back pain, nausea, and diarrhea.
Menorrhagia is characterized by abnormally heavy menstrual bleeding, which can lead to anemia and fatigue. This condition can be caused by hormonal imbalances, uterine fibroids, or polyps, among other factors.
Metrorrhagia refers to abnormal bleeding between menstrual periods, which can be caused by hormonal imbalances, fibroids, or polyps, or in some cases, cervical or endometrial cancer.
Leukorrhea is a condition in which there is an excessive discharge of whitish or yellowish vaginal discharge, which can be caused by hormonal imbalances, infections, or sexually transmitted diseases.